When you discover bed bugs in your home, your first instinct might be to reach for commercial pesticides. But what if you could effectively fight these resilient pests with items you already have around your house? Many common household products can kill or repel bed bugs when used correctly. This comprehensive guide explores home remedies to get rid of bed bugs – using accessible, affordable items that can help you tackle your infestation without harsh chemicals or expensive treatments. In addition to treating your home, it’s crucial to address any potential infestations on your pets. Learning how to eliminate bed bugs on dogs is an essential step in ensuring that your furry friends remain safe and comfortable. With a combination of targeted cleaning and the right home remedies, you can effectively protect both your living space and your pets from these unwelcome invaders.
Top Home Remedies to Get Rid of Bed Bugs

Safe & Natural

Fast Acting

Natural Repellent
- Why Use Household Items to Fight Bed Bugs?
- 1. Baking Soda
- 2. Rubbing Alcohol
- 3. Essential Oils (Lavender & Tea Tree)
- 4. Lysol Spray
- 5. Ammonia
- 6. Boric Acid
- 7. Hot Water & Steam
- 8. Vinegar
- 9. DIY Bed Bug Traps
- Effectiveness Comparison
- Application Tips & Best Practices
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Use Household Items to Fight Bed Bugs?
Before diving into specific solutions, it’s important to understand the advantages of using household items against bed bugs:
Cost-Effective
Professional extermination can cost hundreds or even thousands of dollars. Household remedies typically cost a fraction of this amount, using items you may already have at home.
Immediate Action
When you discover bed bugs, you need to act quickly. Household solutions allow you to start treatment immediately without waiting for professional help or product deliveries.
Reduced Chemical Exposure
Many commercial pesticides contain harsh chemicals that may be harmful to children, pets, or people with respiratory issues. Natural household alternatives can provide safer options.
For best results, use household remedies as part of a comprehensive bed bug management strategy. This may include careful cleaning, decluttering, heat treatment, and ongoing monitoring.
1. Baking Soda
Baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) is one of the most versatile household products and can be an effective weapon against bed bugs when used correctly.

How It Works
- Dehydration: As a salt compound, baking soda can absorb moisture from bed bugs’ bodies, leading to dehydration.
- Microscopic Abrasion: At the microscopic level, baking soda consists of tiny, sharp crystals that can damage bed bugs’ exoskeletons.
- Gas Release: When ingested by bed bugs, baking soda can release carbon dioxide as it breaks down, potentially disrupting their digestive systems.
Application Methods
- Dry Powder: Sprinkle a thick layer around bed legs, along baseboards, and in cracks where bed bugs hide.
- Paste Method: Mix baking soda with water to create a honey-like paste. Apply to bed frames, furniture crevices, and other hiding spots.
- Barrier Method: Create thick piles around furniture legs to force bugs to crawl through it when approaching your bed.
While baking soda can help control bed bugs, it works slowly and is most effective for minor infestations or as a supplementary treatment. Vacuum up and reapply every three days for best results.
2. Rubbing Alcohol
Rubbing alcohol (isopropyl alcohol) is a potent contact killer for bed bugs and is particularly effective when used as a direct spray.

How It Works
- Desiccation: Alcohol rapidly dehydrates bed bugs by dissolving their protective outer shells.
- Nervous System Damage: The harsh compounds can burn bed bugs’ bodies and disrupt their nervous systems.
- Egg Elimination: Higher concentrations of alcohol can penetrate and kill bed bug eggs.
Best Formulations
- 91% Isopropyl Alcohol: Higher concentration provides better killing power (preferable to 70%).
- Mixed Solutions: Combining different alcohols (isopropyl + ethanol) can provide enhanced effectiveness.
- Undiluted Application: For maximum effect, use full-strength rather than diluted solutions.
While effective as a contact killer, alcohol alone will rarely eliminate an entire infestation. Use it as part of a multi-faceted approach, and be extremely cautious about its flammability risks.
3. Essential Oils (Lavender & Tea Tree)
Essential oils offer a natural bed bug treatment. They are pleasant-smelling alternative to chemical pesticides. Lavender and tea tree oils are particularly effective against bed bugs.

| Oil Type | Active Components | Effectiveness | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lavender Oil | Linalool, linalyl acetate | Contact killer; excellent repellent | Spray on fabrics, mattress seams; add to laundry rinse |
| Tea Tree Oil | Terpenes, terpenoids | Strong contact killer; moderate repellent | Direct spray on bugs and hiding places; deeper penetration into crevices |
Lavender Oil Spray Recipe
Ingredients
- 20 drops of pure lavender essential oil (L. angustifolia)
- 10 drops of tea tree oil (optional for enhanced effect)
- 2 cups of water
- 1 tablespoon of dish soap (helps oils mix with water)
Application
- Combine ingredients in a spray bottle and shake well before each use
- Spray directly on mattress seams, bed frames, and furniture crevices
- Apply to sheets and pillowcases before bedtime
- Reapply every 3-4 days
- For enhanced protection, apply to your body as a natural repellent
Tea Tree Oil Spray Recipe
Ingredients
- 25 drops of pure tea tree essential oil
- 2 cups of filtered or distilled water
- 1 tablespoon of dish soap
Application
- Mix in a spray bottle and shake vigorously before each use
- Spray where you’ve seen bed bugs and their common hiding places
- Apply in the morning and again before bed for active infestations
- Store in a cool, dark place between uses
- Effective when sprayed directly on bed bugs
Essential oils can cause skin irritation in undiluted form. Always wear gloves when handling pure oils, and never apply undiluted essential oils directly to your skin. Keep away from children and pets, and test on fabrics before widespread application.
4. Lysol Spray
Lysol disinfectant spray is primarily designed to kill germs and bacteria, but it can also be effective against bed bugs when applied directly.

How It Works
The active ingredients in Lysol disrupt bed bugs’ nervous systems and can suffocate them when applied generously. Lysol is most effective while wet—it kills bed bugs on contact but loses effectiveness once dry.
Best Application
Apply Lysol directly to visible bed bugs and their hiding places. For maximum effectiveness, use after steam treatment while surfaces are still warm and moist, as this helps the spray penetrate deeper into cracks and crevices.
- Readily available in most households
- Dual purpose: disinfects while killing bed bugs
- Safe for use in children’s rooms when used as directed
- Effective on low-level infestations
- No need to discard treated items
- Contains chemicals that require careful handling
- Only works when wet; limited residual effect
- Potential respiratory irritant; ensure proper ventilation
- May not penetrate deeply enough to reach all hiding bed bugs
- Not effective against eggs unless directly sprayed
5. Ammonia
Household ammonia is a strong cleaning agent that can also be employed as a bed bug killer, though it requires careful handling due to its strong fumes.

How It Works
Ammonia is toxic to bed bugs through both contact killing and fumigation effects. It suffocates bed bugs and can penetrate their exoskeletons, leading to death. However, it’s most effective when bed bugs are directly exposed to the solution.
Application Method
Dilution Ratio: Mix 1 part household ammonia with 1 part water in a spray bottle. Shake well before using.
Target Areas: Spray along baseboards, in cracks, on bed frames, and other hiding spots. For enhanced effectiveness, some users combine ammonia with alcohol for a more powerful solution.
NEVER mix ammonia with bleach or products containing bleach! This combination creates toxic chloramine gas that can be lethal. Always ensure proper ventilation when using ammonia, and keep children and pets away from treated areas until completely dry.
6. Boric Acid
Boric acid is a naturally occurring compound found in volcanic waters and hot springs. Available as a white powder, it has long been used for pest control.

How It Works
As a desiccant, boric acid damages bed bugs’ waxy protective coating, causing them to dehydrate slowly. While not as fast-acting as some treatments, it provides longer-lasting protection against reinfestation.
Application Methods
- Dry Application: Sprinkle boric acid around and in infested areas, especially cracks, holes, and deep corners.
- Spray Solution: Dilute in water and spray on baseboards and other areas (less effective than dry).
- Laundry Additive: Use borax (a boric acid derivative) in hot water to wash infested bedding.
- Steam Combination: Apply after steam treatment for enhanced penetration and effectiveness.
- Inexpensive and readily available
- Long-lasting residual control
- Bed bugs cannot develop resistance to its physical mode of action
- Does not repel bugs, so they continue their normal activities while being exposed
- Less effective than other options when used alone
- Leaves a white residue that can be difficult to clean
- Potential health risks with excessive exposure
- Not recommended for use on mattresses or upholstery
- Slow-acting compared to contact killers
Boric acid works best as part of a comprehensive bed bug treatment plan rather than as a standalone solution. It’s particularly effective in preventing reinfestation after other methods have reduced the bed bug population.
7. Hot Water & Steam
Heat is one of the most effective natural bed bug killers. Hot water and steam can penetrate fabrics and crevices to kill both adult bed bugs and their eggs.

Heat treatment is one of the few methods that can kill 100% of bed bugs and their eggs when applied correctly. Unlike chemical treatments, bed bugs cannot develop resistance to heat.
8. Vinegar
Common white vinegar contains acetic acid, which can be harmful to bed bugs when applied directly.

How It Works
The acetic acid in vinegar damages bed bugs’ nervous systems and can dissolve their exoskeletons on contact. While not as potent as commercial pesticides, vinegar is non-toxic to humans and pets.
Application Method
- Mix equal parts white vinegar and water in a spray bottle
- Spray directly onto bed bugs and their hiding places
- Apply to mattress seams, box springs, bed frames, and crevices
- Reapply frequently as vinegar evaporates quickly
Vinegar works best on early infestations and as a supplementary treatment. The strong smell dissipates as it dries, but some people find the odor unpleasant during application. Adding essential oils can help mask the smell while enhancing effectiveness.
9. DIY Bed Bug Traps
Homemade traps can help monitor bed bug activity and reduce their population by capturing them as they attempt to reach their host.
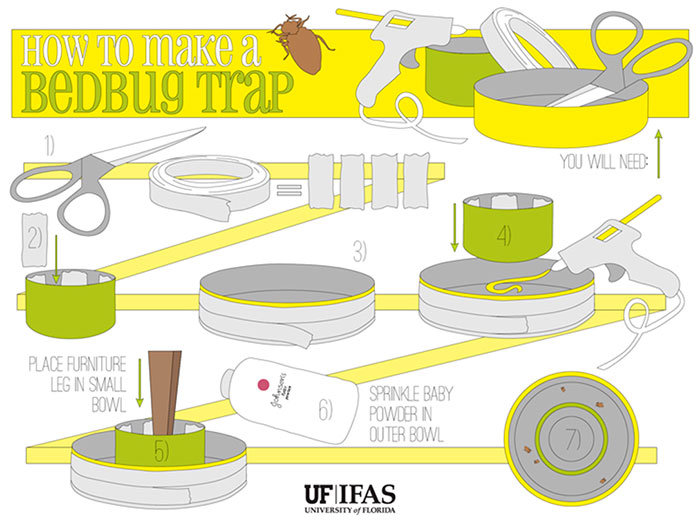
DIY CO₂ Trap Instructions
- Place a smaller plastic container inside a larger one and secure it with tape
- Mix 2 cups of sugar with 2 liters of warm water and add ½ teaspoon of yeast
- Pour the mixture into the inner container
- Tape the outer edges of the large container and create “tape paths” down the sides
- Apply baby powder to the inner walls of the outer container to prevent escape
- Place traps near bed legs or suspected bed bug activity areas
Traps are most effective for monitoring and as part of an integrated pest management approach. They’re unlikely to eliminate an infestation on their own but can help confirm the presence of bed bugs and track the effectiveness of your treatment efforts.
Effectiveness Comparison
Not all household remedies are equally effective. This comparison can help you choose the best options for your situation.
| Household Item | Killing Power | Residual Effect | Egg Killing | Safety Rating | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubbing Alcohol (91%) | High (Contact) | None | Moderate | Medium (Flammable) | Quick spot treatment |
| Essential Oils | Medium | 1-3 days | Low | High (Diluted) | Natural repellent |
| Lysol Spray | High (Contact) | Minimal | Medium | Medium | Accessible solution |
| Boric Acid | Low | Weeks | Low | Medium | Long-term control |
| Ammonia | Medium-High | None | Medium | Low (Fumes) | Severe infestations |
| Baking Soda | Low | Until vacuumed | Very Low | Very High | Safe preventative |
| Hot Water/Steam | Very High | None | Very High | High | Complete elimination |
| Vinegar | Medium | None | Low | Very High | Early infestations |
| DIY Traps | Low | Until full | None | Very High | Monitoring progress |
Application Tips & Best Practices
For maximum effectiveness with household remedies, follow these essential guidelines:
Integrated Approach
Use multiple methods simultaneously rather than relying on a single solution. For example, combine heat treatment with essential oil sprays and monitor with traps.
Consistent Application
Most household remedies require frequent reapplication. Create a schedule and stick to it—daily application for active infestations, weekly for prevention.
Thorough Coverage
Bed bugs hide in tiny cracks and crevices. Be meticulous in your application, targeting seams, tufts, frames, baseboards, and any potential hiding spots.
If your infestation persists despite consistent application of household remedies for 4-6 weeks, or if it’s spreading to multiple rooms, consider consulting a professional. Some infestations are too severe for DIY approaches alone.
Conclusion
Household items can be effective weapons in your fight against bed bugs, especially when used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. While they may not work as quickly as professional treatments, these accessible, affordable solutions offer a valuable first line of defense and can successfully eliminate minor to moderate infestations.
The most successful approach combines multiple methods: heat treatment to kill bugs and eggs, contact killers like alcohol or Lysol for visible bugs, residual treatments like boric acid for long-term control, and ongoing monitoring with traps. With persistence and thorough application, these household remedies can help you reclaim your home from these persistent pests.
Remember that bed bug elimination is a marathon, not a sprint. Stay vigilant, be thorough in your applications, and don’t give up—with time and consistent effort, you can successfully eliminate bed bugs using DIY bed bug solutions and other home remedies.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to eliminate bed bugs with household remedies?
Complete elimination typically takes 2-6 weeks when using household remedies, depending on the severity of the infestation and consistency of treatment. Expect to see a gradual reduction in bug activity rather than immediate results. Continue treatments for at least two weeks after the last sighting to ensure all eggs have hatched and been eliminated.
Can household remedies kill bed bug eggs?
Most household remedies are more effective against adult bed bugs than eggs. Heat (temperatures above 120°F) is the most reliable method for killing eggs. Steam treatment, washing in hot water, and high-heat drying can effectively eliminate eggs. Chemical treatments like rubbing alcohol and Lysol can kill eggs upon direct contact but may not penetrate egg casings completely.
What’s the most effective household item for killing bed bugs?
High heat (steam or hot water) is the most effective household method, killing all life stages including eggs with nearly 100% effectiveness when applied correctly. Among chemical options, 91% isopropyl alcohol provides the quickest kill on contact, though it lacks residual protection. For best results, combine heat treatment with targeted application of contact killers and ongoing preventative measures.
Are household remedies safe around children and pets?
Safety varies by product. Natural options like diluted essential oils, baking soda, and vinegar are generally safer but should still be kept away from children and pets. Chemical options like ammonia, rubbing alcohol, and Lysol require careful handling and proper ventilation. Always follow safety guidelines, keep treatments out of reach of children and pets, and allow treated areas to dry completely before reuse.
Can bed bugs become resistant to household remedies?
Bed bugs can develop resistance to chemical insecticides but cannot develop resistance to physical killing methods like heat, desiccants (boric acid, diatomaceous earth), or mechanical traps. This gives household remedies an advantage over some commercial pesticides. Rotating different treatment methods further reduces the chance of resistance developing.




Hi Inga,
I am the cleanest person in the world. I clean my apartment just about every day. I cannot understand why I would have such a nasty bug in my apartment. How do I know if I really do have these bugs? I have these red bumps meanly on my feet and legs, and some on my thigh. They look like red bumps that itch.
Sincerely,
Help!
Hi there, I totally understand how frustrating and confusing this can be! Bed bugs don’t care about cleanliness, unfortunately. They can hitch a ride into even the most spotless homes through luggage, clothes, used furniture, or even guests.
Red, itchy bumps on your feet and legs can be a sign of bed bugs, but they can also come from fleas, mites, or even a skin reaction. To be sure, try checking along mattress seams, behind headboards, and in small cracks for tiny black spots, shed skins, or the bugs themselves. As a quick DIY check, try placing double-sided tape around the edges of your mattress or under your bed legs to catch any bugs. You can also use a flashlight to inspect seams, mattress tags, and cracks near your bed for tiny rust-colored spots or shed skins.